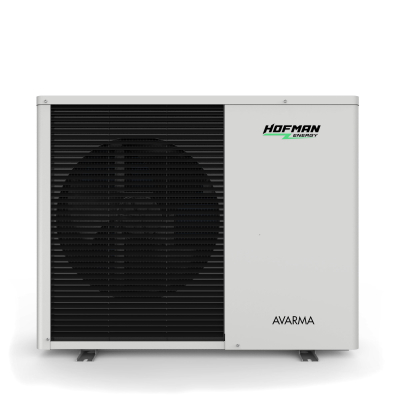
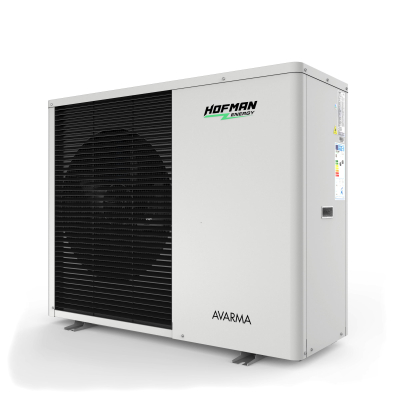
Heat pumps
- SKU:
- HE-AI-50013065
- Shipping weight:
- 5,80 kg
- Item weight:
- 5,50 kg
- SKU:
- HE-TE-P30-1S
- Shipping weight:
- 5,80 kg
- Item weight:
- 5,50 kg
Invest in green technologies with the heat pumps from HOFMAN-Energy
Heat pumps are innovative devices that save on heating costs while being environmentally friendly. Among the most well-known is the air to water heat pump, which uses air as a heat source based on inverter technology. The heat pump principle involves absorbing the low-temperature heat from the environment and raising it to a higher temperature level for domestic heat in buildings.
Heat pumps thus make an essential contribution to the energy transition and promote a green, sustainable lifestyle. At HOFMAN-Energy, we offer a range of these environmentally friendly solutions, perfect for workshops and hobby DIY enthusiasts who want to actively support renewable energies.
How does a heat pump work?
Heat pumps use the principle of heat transfer to save on heating costs. Simply put, a heat pump takes energy from the outside air and transfers it to the house's heating system. The air-to-water heat pump is specifically designed to absorb this energy and transfer it into a water system to generate heating and hot water. With this sustainable heating system, you can save a considerable amount of heating costs.
What is inverter technology?
Another highlight that distinguishes our air to water heat pump is the inverter technology. Thanks to it, the devices can not only heat up faster and more efficiently, but also adapt their performance to the current heat needs. This means that the pump works more energy-efficiently and expensive energy waste is avoided.
Why Air-to-Water Heat Pumps are Environmentally Friendly
In addition to energy savings, air-to-water heat pumps offer another key advantage: they are extremely environmentally friendly. Given that they mainly rely on renewable energy sources, they play a significant role in reducing CO₂ emissions and decreasing our planetary footprint. As they use air as a heat source, they are virtually unlimited and don't lead to environmental pollution or resource depletion.
How long does a heat pump last?
Heat pumps are designed to be long-term solutions for your heating needs. On average, heat pumps last about 15 to 20 years. With regular maintenance and good care, this lifespan can often be surpassed. The principle of heat pumps and the technology used play a crucial role in this.
Our heat pumps, based on inverter technology, compensate for energy loss by transferring the heat generated to the heating system. They not only work efficiently but also help to save on heating costs and protect our environment. Remember, any investment in an eco-friendly heating system is an investment in the future: both in terms of the performance and lifespan of the device, as well as our planet.
What does a heat pump look like?
A heat pump resembles a boxy outdoor central air conditioner. Essentially, an air source heat pump, especially the monoblock heat pump we have at HOFMAN-Energy, consists of two main parts: an indoor unit and an outdoor unit. The outdoor unit, often grey or white, contains the compressor, responsible for sucking in air and compressing it to draw out the heat. The indoor unit resembles a regular central heating boiler, often wall-mounted. It handles warming up the water once the heat has been extracted - this hot water is then sent around your home to heat it. Thus, our air to water heat pump is not only practical and efficient but also compact and unobtrusive in design.
Funding opportunities for your air-water heat pump
Looking for an environmentally friendly heating solution? With an air-water heat pump, you can not only actively contribute to the energy transition, but also benefit from attractive government subsidies. Since heat pumps contribute significantly to reducing CO₂ emissions and saving heating costs, many countries support their installation and operation through a variety of programs.
In the course of the energy transition, inverter technology is increasingly becoming the focus of funding. This is also the case in Austria: Here you can apply for financial support for the installation of your air-water heat pump.
Funding Opportunities for Your Air-Water Heat Pump
Are you in search of an eco-friendly heating solution? Not only can you actively contribute to the energy transition with an air source heat pump, but you can also benefit from attractive government subsidies. Since heat pumps contribute significantly to reducing CO₂ emissions and saving heating costs, many countries support their installation and operation through various programs. As part of the energy transition, inverter technology is increasingly coming into focus for funding.
Contribute to your personal energy transition with HOFMAN-Energy Heat Pumps
In our online shop, we present to you our wide range of air-water heat pumps, which not only represent a clear commitment to active environmental protection but also make an important contribution to the urgently needed energy transition. By purchasing and using our products, you are making a statement. This is part of our community of conscious individual and corporate customers committed to green technologies and fighting for a clean and sustainable environment.
Each of our products is designed for the highest energy efficiency, to generate the maximum amount of green energy and actively combat climate change. In our shop, you will therefore find not only heat pumps, but also other sustainable products such as photovoltaic systems or battery storage. Take the first step now and start your personal energy transition with HOFMAN-Energy.
FAQ - Heat pumps
General information
Yes, heat pumps can also be used effectively in old buildings to heat or cool them. However, in many cases, installing a heat pump in an old building requires some adjustments and considerations to ensure the best possible efficiency and performance. Heat pumps are a sustainable and cost-effective heating option, and they can also be a good choice in old buildings if they are planned and installed properly.
A heat pump can make sense in various situations, depending on individual needs and circumstances. Here are some factors and situations in which the use of a heat pump could be recommended:
Heating and cooling buildings
Heat pumps are well suited to heating and cooling residential buildings, apartment buildings, commercial buildings and industrial facilities
Climate zone
Heat pumps are particularly efficient in regions with temperate to cold climates. In areas with long heating seasons, they can significantly reduce energy costs. Energy efficiency: If you are looking for an energy-efficient heating and cooling method, a heat pump is often a good choice. They can use considerably less energy compared to conventional heating systems.
Renewable energy sources
Heat pumps can be coupled with renewable energy sources such as solar energy or wind energy, making them even more environmentally friendly. New build or renovation: heat pumps can be easily integrated into new construction projects as the systems can be planned from the outset. However, they can also be retrofitted in existing buildings.
Reduction of CO2 emissions
If environmental aspects play a role and you want to reduce your building's CO2 emissions, heat pumps are an environmentally friendly choice.
Long-term investment
While heat pumps can initially be more expensive than conventional heating systems, they offer long-term savings on energy costs and can pay for themselves over time.
Yes, combining a heat pump with underfloor heating can make a lot of sense in many cases and offers several advantages:
High efficiency
Underfloor heating systems work with lower flow temperatures compared to conventional radiators. This goes well with heat pumps, which work more efficiently when they operate with lower temperature differences. The combination enables optimum heat pump efficiency.
Even heat distribution
Underfloor heating distributes heat evenly throughout the room, resulting in a pleasant indoor climate. This is particularly desirable in living rooms and bedrooms
Comfort
Underfloor heating systems offer a high level of comfort as they have no visible radiators or air ducts. There are no cold spots in the room and the heat rises gently from the bottom to the top.
Energy savings
Combining a heat pump with underfloor heating can lead to significant energy savings, as the low flow temperatures of the underfloor heating allow the heat pump to work more efficiently. This can lead to lower heating costs.
Cooling function
Many heat pumps also offer a cooling function that can be used for air conditioning in summer. Underfloor cooling can provide comfortable room temperatures without the need for visible air conditioning systems.
However, it is important to ensure that the underfloor heating and heat pump are well matched and installed by a professional. Choosing the right type of heat pump (air-to-water, brine-to-water, etc.) and sizing the system is crucial for efficiency and performance. You should also ensure that your building is sufficiently insulated to minimize heat loss.
Overall, combining a heat pump with underfloor heating is an efficient and convenient solution that can be useful in many applications, especially in well-insulated buildings or new builds.
Choosing the right heat pump depends on various factors, including your specific requirements, the climate in your region and building characteristics. Here are some common types of heat pumps and their applications:
Air-to-water heat pumps
Suitable for many applications, especially in areas with mild to cold winters. It extracts heat from the air and transfers it to a water circulation system that is used to heat the building. This type of heat pump is usually easier to install and requires less space than other types.
Salt-to-water heat pumps
Ideal if you have access to a natural heat source in the ground, such as a ground collector or geothermal system. They are very efficient and can work well in areas with extremely cold weather
Air-to-air heat pumps
They heat or cool the air directly and can be used in conjunction with an air distribution system such as ventilation shafts or ducts. This is particularly useful if you want both heating and cooling
Gas absorption heat pumps
Suitable if you live in an area with limited access to electricity as it can run on gas or electricity. It can absorb heat from the environment and is particularly useful in areas with moderate to cold climates.
Hybrid heat pumps
These systems combine a heat pump with a conventional heating system, such as a gas or oil heating system. They offer the flexibility of using the benefits of a heat pump but also having a back-up heating system.
Geothermal heat pumps
They are very efficient as they use geothermal energy. However, they require complex installation and are problematic in urban environments or where space is limited.
When choosing a heat pump, you should consider the specific needs of your building and region. The efficiency and performance of a heat pump will depend on factors such as building insulation, energy requirements, the available energy source and local climate conditions. A thorough consultation with a professional is therefore advisable to determine the most suitable heat pump for your specific situation.
Installing a heat pump usually requires the services of a qualified professional or a specialized installation company. Here are some options for who can install the heat pump in your home:
Heating and air conditioning installer
These are professionals who specialize in the installation of heating and air conditioning systems. They are usually experienced in installing heat pumps and can ensure that the system works properly
Plumbing installer
Some plumbers are experienced in installing heat pumps, especially when connecting the system to the hot water tank.
Electrician
As heat pumps are often electrically powered, it is important to use a qualified electrician to make the electrical connections safely and in accordance with local regulations.
Specialized heat pump installation companies
There are companies that specialize exclusively in the installation of heat pumps. These can offer extensive experience and expertise in heat pump systems
No matter who you choose for the installation, it is important to ensure that the person or company has the necessary qualifications and licenses to carry out the work. This will help ensure that the installation is safe and complies with local building regulations.
Before installation, you should also have a thorough assessment of your building and needs carried out to ensure that the heat pump selected and its size are suitable for your particular situation. Professional advice can help you make the right choice and ensure that your heat pump system works efficiently and reliably.
Sizing a heat pump is an important step in ensuring that it works efficiently and reliably. Here are some steps to consider when sizing a heat pump:
Determine the heat requirement
First, you need to determine the heat requirement of the building that the heat pump is to heat or cool. This requirement depends on various factors, including the size of the building, the thermal insulation, the geographical location and the desired room temperature.
Improve energy efficiency
Before determining the size of the heat pump, it is important to improve the energy efficiency of the building. This can be achieved through additional thermal insulation, the use of energy-saving windows and minimizing heat loss. The less heat the building loses, the smaller the heat pump required can be.
Choosing heat sources
Heat pumps can draw heat from various sources, including the air, ground or groundwater. Choosing the right heat source depends on local conditions and costs. Air source heat pumps are often easier to install, while brine-to-water or water-to-water heat pumps are usually more efficient.
Note the COP (coefficient of performance)
The COP value indicates how efficiently a heat pump works. The higher the COP value, the more efficient the heat pump is. Make sure that the selected heat pump has a good COP value to save energy costs
Determine the size of the heat pump
The right size of heat pump depends on your heating requirements and operating conditions. An experienced installer can calculate the required output of the heat pump to ensure that it can provide sufficient heating or cooling without being oversized.
Consider heating and cooling systems
If you want to use the heat pump for both heating and cooling applications, you need to ensure that it can meet these requirements. Some heat pumps are capable of both heating and cooling, while others are designed specifically for one of these functions
Designing a heat pump usually requires working with an experienced installer or engineer who can take into account the specific requirements of your project. A well-crafted design can ensure that your heat pump operates efficiently and reliably, achieving the desired comfort and energy savings goals.
The proper placement of a heat pump is critical to its efficient and reliable operation. Here are some important considerations when placing a heat pump:
Outdoor unit for air source heat pumps
If you are using an air source heat pump, the outdoor unit is usually located outside the building. Make sure it is placed in a well-ventilated location that allows sufficient airflow to facilitate heat absorption and release.
The location should be protected from strong winds and direct sunlight so as not to impair the efficiency of the heat pump.
Pay attention to sound insulation
Heat pumps can generate noise, especially the outdoor units of air source heat pumps. Make sure that the heat pump is positioned so that noise does not cause a nuisance to you or your neighbors.
If necessary, soundproofing measures can be taken to reduce noise levels.
Accessibility for maintenance
The heat pump should be installed in a location that is easily accessible so that maintenance work and any repairs can be carried out easily.
Regular maintenance is important to ensure the service life and efficiency of the heat pump
Compliance with local regulations
Make sure that the installation of the heat pump complies with local building laws and environmental regulations. This may relate to distances from property boundaries and buildings as well as other requirements.
The exact placement of the heat pump depends on various factors, including the type of heat pump, the local conditions and the structural features of your property. It is advisable to consult a professional who can help you choose the best location and properly install your heat pump.
The use of a buffer tank offers several advantages:
Efficiency
A buffer cylinder allows the heat pump to operate continuously, even when the heat demand in the building is low. This can increase the efficiency of the heat pump as it can work in a stable operating mode.
Avoidance of short cycles
The buffer tank prevents frequent switching on and off of the heat pump, which can contribute to a longer service life of the heat pump.
Flexibility
A buffer cylinder makes it possible to store excess heat that can be used later when the heat demand increases.
It is important to choose the right size of buffer cylinder for your system to ensure that it can store sufficient heat. A heating engineering professional can help you select and install a buffer tank for your heat pump to ensure your heating system works efficiently and reliably.
Sizing a heat pump is an important step in ensuring that it works efficiently and effectively in your heating or cooling system. Correct sizing depends on various factors that need to be taken into account:
Heat requirement of the building
The heat requirement of your building is one of the most important factors when dimensioning a heat pump. This requirement depends on the size of the building, the thermal insulation, the geographical location and the desired room temperature. A thorough heat demand calculation is crucial to determine the right size of heat pump.
Climatic conditions
The climate in your region has a significant impact on the performance of the heat pump. In regions with very cold weather, you may need a larger heat pump to generate sufficient heat.
Heat distribution system
The system used to distribute the generated heat in the building also influences the dimensioning of the heat pump. For example, radiant heating systems require a lower flow temperature than convection heating systems.
How the heat pump works
Different types of heat pumps (e.g. air-to-water, brine-to-water, water-to-water) have different performance profiles and efficiency levels. Make sure you choose a heat pump that suits the requirements of your building
Seasonal variation
Consider the seasonal variation in heating or cooling demand. A heat pump should be able to operate efficiently in both extreme winter cold and moderate temperatures.
Additional loads
If your heat pump is also used to heat water or for other purposes, these additional loads must be taken into account when dimensioning.
COP (coefficient of performance)
Consider the COP value of the heat pump. A higher COP means higher efficiency. Heat pumps with a higher COP can generate more heat or cold with lower power consumption.
Reserve capacity
It is advisable to choose a heat pump with a certain reserve capacity to ensure that it can generate sufficient heating or cooling even in extreme situations.
The exact sizing of a heat pump often requires working with a professional who can perform a heat demand calculation and recommend the right heat pump for your specific scenario. A heat pump that is too large or too small can be inefficient and lead to higher running costs, so it is important to approach this task carefully.
A heat pump is a technical device that is used to transport heat from a lower temperature location to a higher temperature location. The main principle of the heat pump is based on the second law of thermodynamics, which states that heat does not flow from a warmer place to a colder place by itself unless work is done. Heat pumps use these thermodynamic principles to extract heat from a lower temperature environment and transfer it to a higher temperature environment.
Here is a basic explanation of the principle of the heat pump:
Evaporation
A refrigerant circulates through the heat pump in a closed circuit. First, the refrigerant evaporates at low temperature and low pressure by absorbing heat from the environment. This process takes place in an evaporator.
Compression
The vaporized refrigerant is then fed into a compressor, where it is pressurized. This increases its temperature considerably.
Condensation
The heated refrigerant is then passed through a condenser, where it releases heat into the environment and condenses, becoming liquid again.
Expansion
After condensation, the refrigerant is passed through an expansion valve, causing its pressure and temperature to drop sharply. It is fed back into the evaporator to repeat the cycle.
The key to a heat pump's efficiency lies in its ability to move heat from a colder place to a warmer place by applying work (in the form of mechanical energy to the compressor). Since most of the heat energy comes from the environment, a heat pump is an extremely efficient way to heat or cool rooms, as it requires less electrical energy compared to pure electric heating.
Heat pumps are used in various applications, including heating buildings, heating water and air conditioning. They are environmentally friendly as they consume significantly less energy than conventional heating and cooling methods, especially when powered by renewable energy sources.